UP TO THE MINUTE
9 types of low-slope roofing

By KARNAK.
Explore the different types of materials used for flat roofs and why they are used.
There are a variety of materials designed to be used on low-slope or flat roofs. This includes built-up roof (BUR), modified bitumen (mod-bit), concrete, TPO, EPDM, PVC, metal and green roofing. Contrasting this are steep-sloped roofs, which usually have asphalt, tile or metal shingles. These flat roof materials stand out for their installation and usability post installation. Unlike a more traditional shingle, they provide a practical and versatile space, such as outdoor living areas, green roofs and solar panels.
Each of these roof materials has its own benefits, and their own challenges. But it can quickly become overwhelming when you are faced by the sheer number of options. And the industry keeps pushing forward, developing new materials and installation practices for roofers. Before you try and decide what to use on your next low-slope project, check out these options that KARNAK collected.
1 - Built-up roofing (BUR)
Built-up roofing, also known as BUR, is a traditional flat roofing material that consists of multiple layers of asphalt and felt or fiberglass mats. These layers are applied in alternating fashion and then topped with a layer of gravel or a reflective coating. BUR is an affordable and durable option that can last up to 30 years with proper maintenance. However, it requires professional installation and may emit harmful fumes during installation. If you recall the roof top scene in the Shawshank Redemption, they were installing a Built-up roof using the "hot mop and kettle" method.
2 - Modified bitumen roofing
Modified bitumen roofing is a type of asphalt roofing that has been modified with rubber or plastic additives to improve its flexibility and durability. It comes in rolls that are applied to the roof with heat or adhesives. When applied with heat, or fire-emitting torches, it is commonly called the "torch-down method." Modified bitumen roofing is easy to install, repair and maintain, and can last up to 20 years. The main drawback is that it requires regular inspections to prevent leaks.
3 - Concrete roofing
Concrete roofs are installed by pouring concrete into molds on the rooftop to create a smooth surface. Since it has no seams, like most other flat roof types, there are no weak failure points on the open field section of the roof for water to leak through. Concrete roofing is highly durable and may last up to 50 years. It is so durable that it can withstand high winds, insect damage, rot, intense hail, and even fire. The drawback with concrete roofing is that due to its porous nature, it begins to absorb moisture as soon as it is installed. Once it is time to reroof or coat the roof, this moisture will get trapped inside the roof material and potentially cause problems to the new roof surface like blistering.
4 - TPO roofing
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) roofing is a single-ply roofing membrane that is made of a blend of rubber and plastic materials. It is lightweight, durable, and resistant to UV rays, punctures, and chemicals. TPO roofing is easy to install and maintain and can last up to 30 years. Unfortunately, it may be susceptible to tears and punctures from foot traffic or debris. A common reason for punctures in all types of single ply roofing is debris or hardware (like nails or screws) left on the roof that then get stepped on creating small holes through which water can leak.
5 - EPDM roofing
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) roofing is a single-ply roofing membrane that is made of a synthetic rubber material. It is durable, weather-resistant and can withstand extreme temperatures. EPDM roofing is easy to install and maintain and can last up to 50 years. On the downside, it may be susceptible to shrinkage and tenting due to the elasticity of rubber, which can cause leaks and damage.
6 - PVC roofing
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) roofing is a single-ply roofing membrane that is made of a synthetic plastic material. It is durable, fire-resistant and resistant to chemicals and UV rays. PVC roofing is easy to install and maintain and can last up to 30 years. However, it may be susceptible to punctures and requires regular inspections to prevent leaks.
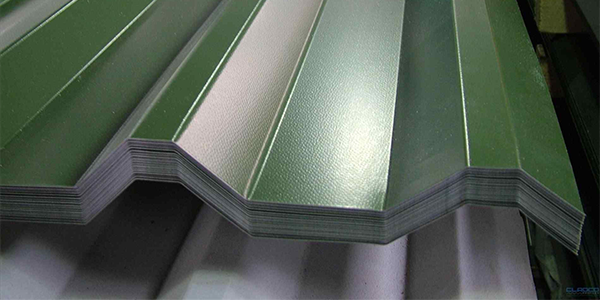
7 - Metal roofing
Metal roofing, while not exactly "flat" perse, would be considered "low slope", as it typically has a slope of 2:12. It is a system of metal pieces seamed together to provide a continuous metal surface. Metal roofs are known for their longevity, durability and energy efficiency. They can be composed of a number of different metals, with common ones being steel (galvanized, galvalume, or factory-coated), aluminum, copper and zinc. Metal roofs can last up to 50 years and require little maintenance, but should be inspected regularly for rust as it can build up in area
8 - Green roofing
Green roofing is a type of flat roofing that incorporates plants, soil, and drainage layers installed over a single-ply roof (TPO, PVC, or EPDM), BUR or Mod Bit roof to create a living roof surface. Green roofing offers numerous benefits, such as reducing stormwater runoff, improving air quality, and providing insulation. The challenge is that it requires specialized installation and maintenance and may not be suitable for all climates or buildings.
9 - Ballasted roofing
Ballasted roofing is a method providing UV and fire protection in the case of BUR roofing and securement of EPDM, TPO, PVC single ply roofs. This eliminates the need for adhesives and fasteners in the field of the roof. The ballast is simply heavy rocks arranged on top of the roof membrane to hold it in place. It is important to note that while this is a surprisingly effective method of holding the membrane in place, it is not allowed in places like Florida where hurricanes may present enough wind and force to send the rocks flying causing damage to surrounding structures.
Conclusion
Choosing the right material for your flat roofing depends on various factors, such as your budget, climate, and building use. Built-up roofing and modified bitumen roofing are traditional and affordable options, while TPO, EPDM and PVC roofing offer superior durability and resistance to weather and chemicals. Green roofing is a sustainable and attractive option but requires specialized installation and maintenance. It's essential to consult with a roofing professional to evaluate your roofing needs and recommend the best material for your flat roof.
Original article source: KARNAK
Learn more about KARNAK Reflective Coatings, Sealants and Cements in their Coffee Shop Directory or visit www.karnakcorp.com.



















Comments
Leave a Reply
Have an account? Login to leave a comment!
Sign In